Empower Your Business With The Magic Of Machine Learning!
- +30 210 9701777
- Aristotelous 83, Athens 163 43
- contact@mobiplus.co
Empower Your Business With The Magic Of Machine Learning!

We are locked into responding and acting in cerain ways.
These quirks or Cognitive Biases have been the subject of much social research by behavioral psychologists such as Daniel Kahneman , Dan Gilbert, Dan Ariely and others.

They have designed ingenious studies to reveal some of our strangest behaviours..
We can use these Cognitive Biases in a positive way in sales and help our client to reach their goal more easily.
The goal of the customer is to be happy with his next purchase!

A fast, automatic, emotional system (System 1)
and a
slow, thoughtful, calculating system that consumes a lot of energy. (System 2)
.
He thus got the Nobel Prize in Economics in 2002.
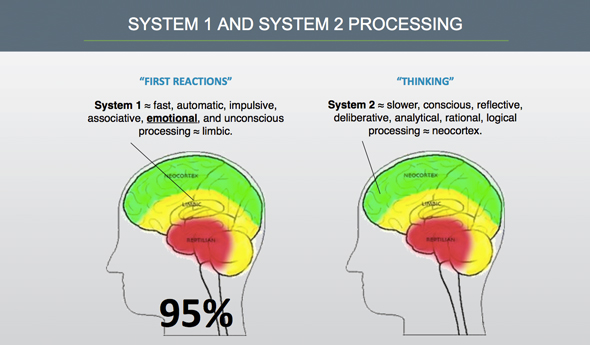
The first is used when making quick or impulse purchases such as clothes and music when adding 2 and 2, and the second is used when considering more rational purchasing situations such as office equipment or tools or when calculating 17 times 24.
E-shops and marketing activities exploit this bias by matching the presentation of a product with the purchase type.
For example, buying clothes is an emotional experience, so the presentation of the clothes targets the emotional thinking “System 1” by focusing on how the buyer will look and feel when wearing the clothes.
On the other hand, functional products, such as a light bulb, aim at rational “System 2” thinking by providing technical details and specifications.
The right linking of the item for sale with the right thought system can have a huge impact on sales numbers.
“Money back guarantee!”
“Not available in stores!”
“Limited number of products !”
“Call now!”
“Only 3 products left!”
These are some of the slogans that exploit our Cognitive Biases. ( cognitive biases ) !
Psychologists and experts from various other fields have identified a wide range of cognitive biases, and each of them affects purchasing decisions differently.
By using the psychological tools we discuss in this article, you can create marketing messages and technologies to positively influence the purchases of your target audience makes.
This cognitive uncovering uses the fact that people draw contradictory conclusions from the same facts when information is presented differently.
This result was originally demonstrated by the Kahneman and Twersky in the 1980s and has since become the mainstay of many companies’ sales strategies.
Behavioural economist Dan Ariely describes this result in his book, “Predictably irrational”, using the example of how The Economist offered three alternative subscription plans.
The first offered access to web content for $59, the other offered access to the magazine edition for $125, and the other offered a combined magazine and web subscription for $125.
Of course, no one chose the “magazine” option.
Most subscribers opted for the combined offer.

Surprisingly, when the magazine-only subscription option was removed from the website, the vast majority of subscribers now chose the web option.
In this case, the presence of an irrelevant option was instrumental in shaping the mindset of subscribers to buy a more expensive option.
E-shops and other advertisements often use this cognitive bias to lead consumers to a particular “middle item” by offering three products;
a product that is cheap but provides little value,
a second product that offers the greatest value,
and a third product that is significantly more expensive than the average option, but provides similar value to the average option.
In confirmation bias, people seek, interpret, and remember information in a way that confirms their existing ideas.
Essentially, people listen to what they want to hear and no matter how unbiased one believes they are, they will favor information that supports what they already believe or want to be true.
Let’s say someone has just bought one of your products.
They decided to buy from you, handed over their precious cash and want to feel that the money was well spent.
This is the post-sale period when customers want to justify their purchase – not only to get their money’s worth but also to protect their egos from admitting they made a bad choice.
The important point here is to communicate to them that they made a good choice, either with a mail, the Thank you in the cart or you made a good choice from the salesperson in the store.
Also reduce the customer’s choices so that they are more satisfied with their choices.
Using shopping recommendation engineering with Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning so that you can guess what he wants to buy and recommend it in the eshop ,in the store ,on his mobile.
Give him a few choices ,up to 7 max , to make his decision easier and he will then be happy with his choice.

Too many choices , make it difficult for him to decide and the most important thing is that after the purchase he is not sure that he made the right choice !
To learn how the top companies in the world increase revenue up to 30% from existing customers using Recommendation Systems and Personalization read the book below.
https://mobiplus.co/ebooks/customer-rediction/
Loss aversion describes how we fear loss much more than we appreciate gaining something of equal value.

For example, we are much more disappointed by losing €10 than we would be happy if we found €10 in our pocket.
We are more disappointed when we lose our home than when we buy a new one.
The classic loss prevention tactic used by businesses is to give consumers free coupons.
Once you give people a €5 voucher, they feel they own that supposed value.
And, if you threaten to take it away , people automatically feel as if they are losing something that is rightfully theirs – even though there is nothing that belongs to them.
Coupons expire in 15 days!
The same happens when a free usage ends.
Users feel like they are about to lose something they have spent the last month using, which makes it harder to give up.
Thanks to loss aversion, you are much more likely to convert free trials into paid subscriptions than converting users who have never used your software before.
That’s why the annual Amazon prime me $99 subscription pushes the subscriber to buy again and again from Amazon.
Last Pieces in the product of interest, 10euro coupon for your next purchase…. are some actions that use the above cognitive bias.
Use Artificial Intelligence and mobiplus shopping recommendation find the product he wants to buy now and recommend it !

This refers to human understanding where, having adopted a view (either as a received view or as an agreement with oneself), one draws on all other evidence to support and agree with it.

Some of the most common factors affecting this cognitive bias include
The best examples that fit this bias are fashion, music, social media, nutrition and elections.
Wearing the same clothes or listening to the same music as others is quite common.
This also applies when you follow the same diet or use the same social network as others.
As for elections, people tend to vote for the candidate they think is most likely to win.
How to use this cognitive bias in e-commerce:
For other cognitive biases see here.
Contact us now to see how the mobiplus shopping recommendation platform can give you the above features and increase your revenue. 30%.
mobiplus member Elevate Greece
Confirmed Innovation.

Test out the Recommendation Engine for up to 20.000 euros in revenue from recommendations. No credit card required. Just enter your company information and we’ll contact you with all the details.